Problem:
Table: CUSTOMER_FIN
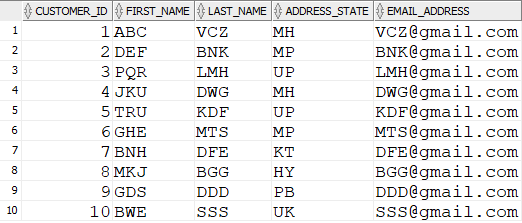
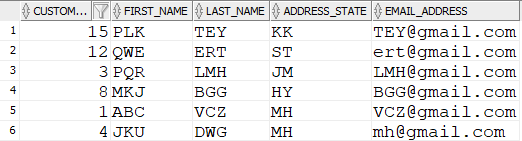
Table: CUSTOMER_RAW
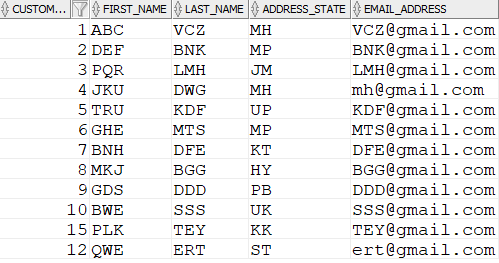
- Either insert data or update data, depending on if it already exists.
- It lets you merge two tables in SQL.
- Called an “upsert”
Use of MERGE Statement
- Where you need to move large amounts of data.
- Combination of INSERT and UPDATE statements, and it’s faster, and easier to code.
- To synchronise data regularly from a source table (e.g. daily, weekly, monthly), and you want to update some record
and insert new records.
Syntax
MERGE INTO table_name
USING table_name
ON (condition)
WHEN MATCHED THEN update_clause
DELETE where_clause
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN insert_clauseMERGE INTO table_name– specify the target table name or view name that you are updating or inserting data into.
USING table_name– This is where you define where the data comes from. It can be a table, a view, or a subquery.
ON (condition)– This is where you specify the condition that determines if the MERGE statement updates or inserts a row.
WHEN MATCHED THEN update_clause– This clause specifies the columns and their new values in the target table.
DELETE where_clause– This clause lets you delete data from the target table after it is updated, if it meets a condition you specify.
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN insert_clause– This clause lets you specify values to insert into the target table,
if the ON condition is not met.
–LOG ERRORS- This clause lets you log any errors that are encountered into a separate table, for you to analyse later.
Insert Only Merge
MERGE INTO customer_fin c
USING customer_raw i
ON (c.customer_id = i.customer_id)
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT (c.customer_id, c.first_name, c.last_name, c.address_state, c.email_address)
VALUES (c.customer_id, c.first_name, c.last_name, c.address_state, c.email_address);Update Only Merge
MERGE INTO customer_fin c
USING customer_raw i
ON (c.customer_id = i.customer_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
c.first_name = i.first_name,
c.last_name = i.last_name,
c.address_state = i.address_state,
c.email_address = i.email_address;Practice Questions:
1.Write an SQL query using the MERGE statement to update employee data in the target table based on matching employee IDs. If a match is found, update the employee’s name and salary; if not, insert a new record.
2. Create a query using the MERGE statement to update the product quantities in the inventory table. If the quantity falls below a certain threshold, insert a new record with details about the low stock.
3. Develop a query that utilizes the MERGE statement to synchronize data between two tables. If a record exists in the source table but not in the target table, insert it. If a record exists in the target table but not in the source table, delete it.
4. Write an SQL query using the MERGE statement to update employee information based on both employee ID and department. If a match is found, update the employee’s salary; if not, insert a new record.
5. Design a query using the MERGE statement to update product prices in the target table based on a subquery that calculates the new prices. If a match is found, update the price; if not, insert a new record.
6. Write an SQL query that employs the MERGE statement to update order status in the target table. If the order amount is greater than a specified threshold, update the status to “High Value”; otherwise, update it to “Regular Value.”
